FOOD IRRADIATION
Home »
Food Preservation by Radiation
A radiation-based technique called food irradiation is used to lower the amount of microorganisms in food. Microorganisms, bacteria, and viruses that are present are either killed, slowed down, or unable to reproduce, depending on the dose. The danger of contracting a foodborne illness is decreased or eliminated with the irradiation method of food preservation. Some foods receive enough radiation to sterilise them and prevent the addition of pathogenic or spoiling bacteria to the final product.
Why is Food Radiated?
Irradiation has a variety of uses. To successfully eradicate organisms like Salmonella and Escherichia coli (E. coli) that cause foodborne sickness, prevention of foodborne illness is essential. Extension of food shelf life through preservation, the destruction or inactivation of organisms that lead to food degradation and decomposition.
Control of Insects:
Pest-control methods harm the food. In such a scenario, the best alternative is eradicating insects without pest-control through the process of irradiation for food preservation.
Delay Ripening and Sprouting:
To prevent premature ripening or sprouting of fruits and vegetables, the irradiation method of food preservation is an ideal approach. Foods can be sterilised by irradiation and kept for a long time without refrigeration. In hospitals, sterilised food benefits individuals with severely compromised immune systems, such as those receiving chemotherapy or those suffering from other life-threatening diseases. Foods that are sterilised using irradiation are subjected to far more treatment than those deemed safe for general consumption.
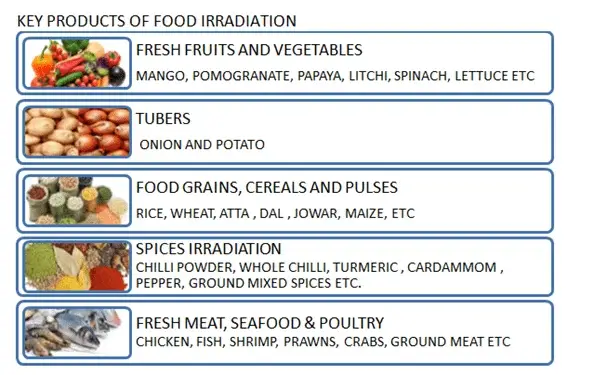
KEY PRODUCTS OF FOOD IRRADIATION
 Currently employed in 55 countries worldwide, with China being the biggest user of Irradiation.
Currently employed in 55 countries worldwide, with China being the biggest user of Irradiation. Several countries such as the USA, Australia, several EU members have mandated irradiation as a phyto-sanitary treatment for food products.
Several countries such as the USA, Australia, several EU members have mandated irradiation as a phyto-sanitary treatment for food products. In 2010 – the USA alone consumed 15,000 metric tonnes of imported fresh produce.
In 2010 – the USA alone consumed 15,000 metric tonnes of imported fresh produce. The main products of irradiation include meat products, fresh fruits like mango, papaya, dragonfruit, pomegranate, vegetables like potatoes and other tubers.
The main products of irradiation include meat products, fresh fruits like mango, papaya, dragonfruit, pomegranate, vegetables like potatoes and other tubers.

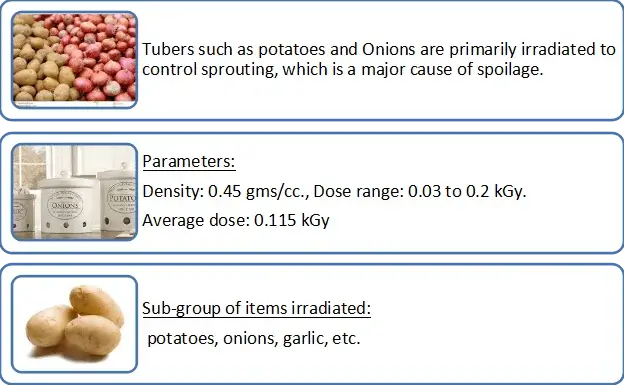
Tubers – Potatoes & Onions
CEREALS & PULSES : RICE , WHEAT, ATTA, DAL

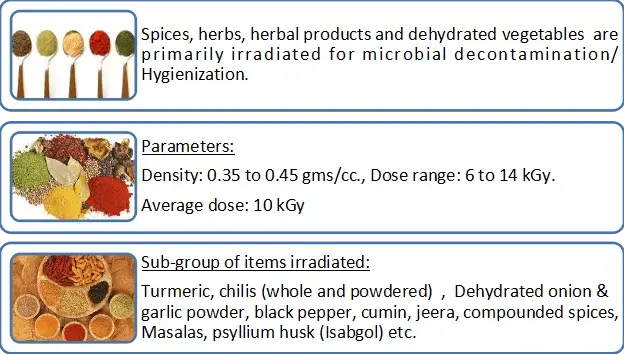
SPICES , HERBS, HERBAL PRODUCTS AND DEHYDRATED VEGETABLES
MEAT & SEAFOOD

Fresh meat and seafood can be irradiated in the chilled condition (2-4 degrees) . These products are currently not irradiated in India, but are commonly irradiated in other parts of the world.
KEY ADVANTAGES/ BENEFITS ARE:
- Shelf life: Extension of shelf life from 2-3 days to 3 to 4 weeks
- Energy savings: Export/ storage of these commodities in chilled condition (2-4oC) as against frozen condition (sub-zero temperatures).
- Improvement in quality: Reduction in the overall microbial load & elimination of drip losses
To Summarise Food irradiation:
- Food irradiation in India is a food processing technique that can increase shelf life and decrease spoiling.
- Foods are subjected to radiation to destroy insects, mould, and microorganisms, yet no measurable radiation levels are left in the food.
- Foods that have been radioactively labelled are done so in compliance with FSSAI guidelines.
Is It Safe to Eat Radiated Food?
For more than 30 years, the safety of irradiation food has been assessed by the FDA, which has determined it as not harmful. The safety of irradiated food has also been acknowledged by the World Health Organisation (WHO), the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
We at Symec Engineers use food preservation by radiation as per the Food Safety Standards in India (FSSAI).
Several foods, including the following, have been authorised for irradiation:
- Pork and beef
- Crustaceans, such as crabs, lobster, and prawns
- Produce that is now in season
- Spinach and Lettuce
- Chicken Seeds for Sprouting (for Alfalfa Sprouts, for example)
- boiled eggs
- Molluscan shellfish, such as clams, oysters, scallops and mussels
- Seasonings & Spices
Amusing Facts about Food Irradiation:
- Food preservation by radiation is used in 55 nations globally, with China being the greatest consumer.
- Irradiation as a phytosanitary treatment for food products has been mandated in a number of nations, including the USA, Australia, and numerous EU members.
- The USA alone consumed 15,000 metric tonnes of fresh food imports in 2010.
- Meat products, fresh fruits and vegetables such as potatoes and other tubers, as well as mango, papaya, dragon fruit, and pomegranate, are among the principal irradiated items.
- Fresh meat and shellfish can be radioactively treated when they are refrigerated (2-4 degrees). However, these products are currently not available for food irradiation in India but are a widespread irradiation practice in other parts of the world.
How to identify if the food has been exposed to radiation?
The goods that undergo radiation should showcase the global radiation sign per the FDA mandate. The food label mentions “Treated by irradiation” or ” Treated with radiation”, along with the Radura symbol next to it, the international symbol identifying food irradiated products. Bulk items like fruits and vegetables must either have a label next to the selling container or be individually labelled. The FDA does not mandate the labelling of specific components in foods with several constituents, such as spices.
It is imperative to keep in mind the food handling procedures used by processors, producers, and consumers are not a substitute for irradiation for food preservation. Because they could still be contaminated with disease-causing microorganisms, irradiated foods must be handled, stored, and prepared in the same manner as non-irradiated foods. If the fundamental guidelines for food safety are not followed, organisms may still exist after radiation.
Our Happy Clients

© 2024 Symec Engineers (India) Pvt. Ltd. All Rights Reserved

 Currently employed in 55 countries worldwide, with China being the biggest user of Irradiation.
Currently employed in 55 countries worldwide, with China being the biggest user of Irradiation.









